What Is QoS (Quality of Service)? Meaning, Working, Importance, and Applications
QoS measures network performance and enables the network to run high-priority apps and services.
Quality of service measures the performance of telephony, computer network services, or cloud and the tools/technologies that guarantee the network’s capability to run high-priority operations. This article explains how QoS works, its importance in networking, and the top QoS applications in 2022.
Table of Contents
What Is QoS?
Quality of service is defined as a measurement of the overall performance of telephony, cloud, or computer network services and the tools/technologies that guarantee the network’s ability to run high-priority operations.
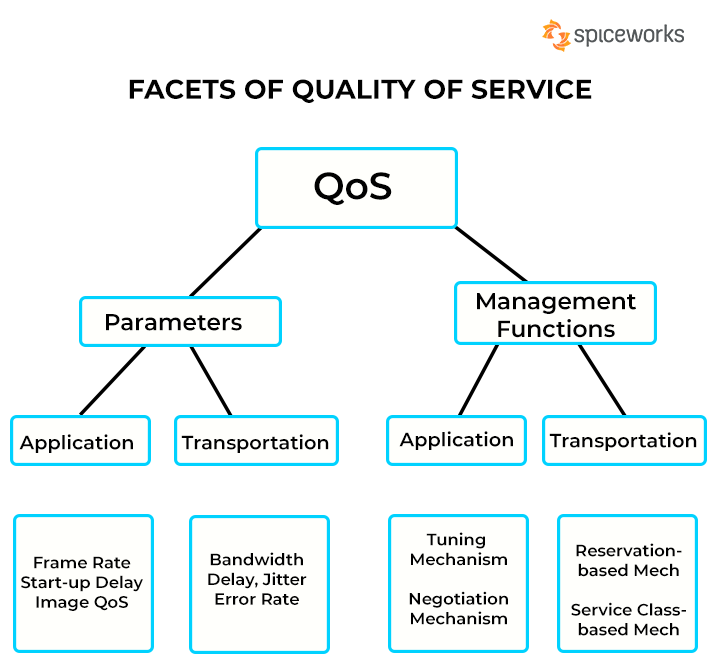
Facets of Quality of Service (QoS)
In the present state of internet and communication network infrastructure, quality of service (QoS) is becoming increasingly crucial to every user. Quality of service is vital across all internet protocol networks, both video and voice streaming and is now very critical to the rising Internet of Things (IoT) field. This article describes QoS, its importance, how it works, and how it has been applied to current needs, modifying your user experience.
Quality of service or QoS means regulating network resources to minimize the degree of packet loss, network jitters, and latency. Quality of service accounts for the technology needed to manage and oversee the movement and transmission of data over a network to reduce the incidence of jitter and packet loss. QoS manages network resources in setting multiple data transmission needs by prioritizing the communication of specific data types.
Quality of service describes and measures a network service’s holistic performance or quality of output. This can be a telephone company providing voice service, a computer network, or even a cloud computing network. The network’s performance is measured in terms of the degree of efficiency experienced by the end-users and not the service providers. QoS can be quantitatively measured using parameters such as packet loss, bit rate, transmission delay, jitter, throughput, availability, etc.
However, when it comes to packet-switched telecommunication networks like telephone and computer networks, QoS is instead used to describe traffic management, prioritization, and resource conservation as opposed to meaning the actual quality of calls or video streaming.
Several organizations provide delay-sensitive services such as real-time video and voice communications. These enterprises make use of QoS to meet up with the traffic requirement of these data types.
Quality of service can also be referred to as the class of service (CoS). But these two concepts are not wholly the same. Class of service takes a less granular approach to traffic management than QoS. However, many people mean the same thing when referring to either concept. Organizations that aim to achieve QoS can do so using some tools and techniques like jitter buffers. But most organizations have QoS included as part of their agreement with their service provider to ensure a minimum performance level.
What does Quality Of Service apply (QoS) to?
QoS is used chiefly by networks that oversee data traffic for resource-intensive systems. These services include internet protocol TV, online gaming, video conferencing, voice over internet protocol (VoIP), video and audio streaming, and video on demand. Quality of service also applies to IoT industries, business organizations, and individual end-users.
The different QoS tools available have similar functions they carry out without being dependent on the administrator. These functions include classification, queuing, policing, shaping, weighted random early discard (WRED), fragmentation, and compression.
How Does Quality of Service Work?
QoS can easily be likened to how an ambulance can navigate congested traffic conditions. However, to adequately understand the concept, we would first discuss the parameters implicated in the quality of service. QoS parameters are used to measure QoS quantitatively and include:
- Packet Loss: Packet loss describes the dropping of data packets during real-time or live communication. This can occur when network bands become over congested and unable to transmit all data packets. Packets are dropped when the queue waiting for transmission becomes more than the network can carry. This can easily lead to breaks in transmission during voice or video calls.
- Latency: Latency is the total time required by a packet in transmission from the source IP address to the destination. In an ideal computer network, latency should be very close to zero, meaning there should be no delay in packet transmission. High latency periods when using VoIP services can lead to disruption with echoing and overlap.
- Jitter: Jitter in internet protocol networks means a variation in latency of a data packet on a network band. This occurs due to network congestion, timing drift, and changes in the route. Excess jitter in a real-time video or voice communication network can be very problematic.
- Mean opinion score (MOS): As the name implies, it’s a score to rate the QoS experienced. The rating can be any figure from one to five. A score of five indicates excellent quality of service.
- Bandwidth: Bandwidth is the volume and maximum amount of information transmitted over a network communication system at a given time or over a while. Often measured in megabytes per second (Mbps), it should not be mistaken for speed. QoS aims to optimize bandwidth by prioritizing and allocating resources to more time-delay sensitive data packets.
Whenever an organization uses its network to transmit data between end locations, the information is first broken down into bits called packets, similar to the way the post office works. These packets are organized by the computer and then transferred over bandwidths in the network.
QoS tools are used to manage and prioritize packets. This is necessary to get maximum efficiency from the bandwidths available for use. Every network has a limited amount of bandwidth. Yet, at different points, they can have a very high influx of data packets to transmit. However, a network can only send a limited amount of information at any time. Thus, QoS tools must select some packets over others for faster transmission during traffic overload.
A typical example is the packets that make up the data transmitted during a video call. These packets are prioritized if there’s traffic congestion over lower priority packets such as Whatsapp messages, Facebook notifications, or email messages. A data packet distributed during video conferencing or a voice call needs to be transmitted as soon as they’re added to the bandwidth. This is because video and voice calls are real-time events that one must synchronize. If packet loss is experienced during a video conference, it can lead to serious communication breaches and a bad user experience. The user can experience jitters or latency.
However, for non-real-time events such as emails or Facebook notifications, a dropped packet will hardly cause any notable communication breach or compromise email security. Instead, immediately the bandwidth becomes less congested, the packets will be reassembled, and the user will still receive their email. Thus, the user has seamless streaming or video experience and still gets all other information when there is high data traffic.
QoS technologies perform the role of allocating flows in traffic. The network administrator can also determine the order in which packet transfer will be handled and how much bandwidth should be given to specific data types. For this to be efficient, the technology must be able to identify each service type.
After identifying service types, it configures routers to create virtual queues for each depending on the priority level. Certain services that are marked as priority access have reserved allocation on the bandwidth whenever the need arises. The markers used to identify the service types of packet representation are located on packet headers. These bits of information inform the QoS tool on what is inside the packet. The title also contains information on the destination IP address and the purpose or use case of the packet.
See More: 5G vs. Fiber Optics: Which One Suits IoT Connectivity the Best?
Importance Of QoS In Networking
QoS is a technology and concept crucial in any business field requiring any type of communication. In the past, businesses had networks operating independently as separate entities. One network was responsible for handling phone calls and teleconferences.
The other network connected computers – laptops, desktops, faxes, etc. In this way, both networks rarely got mixed up, save for some unique circumstances like when a computer uses the telephone line to access the internet. Also, in the past, speed was not a critical factor in networking. The ability of a network to transfer data was all that was necessary. This, however, is not the case anymore. Interactive applications like audio and video are now commonly used and need to be transmitted with high speed and as minimal variation as possible.
This is why QoS is essential. It enables companies to function effectively, providing a secure network for data transfer. QoS helps companies and organizations make maximal use of their existing bandwidth without paying for a new network with a larger bandwidth.
In particular, QoS is necessary to ensure the high performance of critical and inelastic applications that have maximum bandwidth requirements and minimum latency limits and are very sensitive to jitter and packet loss. As earlier mentioned, VoIP and video conferencing are classic examples of these applications.
Quality of service helps a business organization prevent delays in transmitting these sensitive packets. It ensures that the user experience is as expected. Also, QoS makes the network adaptable. More people, devices, and computers are loaded into networks daily. Without quality of service technology and tools, it would be pretty difficult to satisfy all the network demands of subsidiaries. Thus by prioritizing, the end-user experience does not suffer despite an increased amount of users plugged into the network.
The importance of QoS goes beyond business networks. As the internet of things grows with every passing day, there is a greater need for data traffic control and management. Machines now also have access to network bandwidths and must provide real-time status updates to the administrator.
Delay in data transmission due to traffic congestion might make the company or end-user miss out on critical information, fail to resolve rising issues, or prevent damage. Thus, IoT also needs quality of service to ensure information flow is smooth and precise and generates rapid response when necessary.
Applying QoS technology in the IoT industry goes beyond manufacturing or businesses to large-scale smart cities, smart buildings, weather control and monitoring, road traffic monitoring, etc. In summary, the importance of QoS includes:
- Mission-critical applications can access the resources they need in terms of transmission
- Better management of traffic by administrators
- Reduce costs for organizations by eliminating the need for purchasing new network bandwidths
- Facilitating the transfer of important, real-time information from smart devices in IoT
See More: What Is Ailing IoT Implementations at Scale and Ways to Fix Them
Top 7 QoS Applications in 2022
QoS has found its application in several areas. They include:
1. Application classification and data sorting
Quality of service tools can classify different data types according to data types. Several QoS tools classify the applications trying to pass through a network. They allow different classes to receive different levels of priority and treatment. This mechanism includes two techniques applied together to prioritize and manage network traffic.
First, classification tools assess the data types with every packet by using the packet header and then segregate each one according to type, including VoIP, etc. Once the packet has been classified, the marking process takes place.
Sorting a packet implies marking it, enabling devices on that network to determine its priority level. Packets with a high-priority mark will be transmitted over low-priority marked packets whenever traffic congestion occurs. This mechanism is mainly used to manage the orchestration of network hardware components like routers, switches, and access points.
2. Congestion management and avoidance
Congestion management means the evaluation of markings on a packet and queuing them on the basis of detailed algorithms.
Congestion avoidance, however, helps monitor network traffic to pinpoint at-risk areas from becoming congested. When such areas are identified, the congestion avoidance mechanism of QoS tools will drop packets with low-priority to ensure that high-priority packets are retained at that particular time.
Congestion management and avoidance help prevent a network from being overloaded. This is done by using a packet disclosing policy. By managing congestion, high-priority services are first processed and transmitted. Congestion refers to slow data forwarding and delays due to insufficient resources. It leads to delays in packet transmission, a low throughput rate, and a high degree of consumption of resources.
Congestion usually limits the quality of users’ experience of a network. Therefore QoS resolves network congestion from two angles. First, by avoiding congestion and managing existing congestion.
3. Link efficiency to maximize bandwidth use
Although not particular to QoS technology, link efficiency is indispensable to service optimization. Link efficiency to maximize bandwidth use is another application of quality of service.
Bandwidth management is critical to the current generation of applications running on the internet. These applications like VoIP and video-on-demand sites need to be managed appropriately. QoS bandwidth management features a wide range of differentiated services, including defining minimum throughput, guaranteeing minimum throughput, and preventing packets from exceeding a specific size on the communication link. Examples include the real-time transport protocol and transmission control protocol (TCP).
See More: What Is Distributed Computing? Architecture Types, Key Components, and Examples
4. Prioritizing real-time applications
QoS technology is also applicable when there is a need to prioritize real-time applications. This is often an issue in companies, teams, organizations, and industries that use teleconferencing, voice calls, and other communication applications to host critical or managerial business meetings. In today’s remote work, quality of service has proven to be an absolute necessity.
5. Use in resource-intensive applications like video streaming
Quality of service is used in resource-intensive applications such as video streaming. Several companies, such as Netflix, YouTube, and Instagram, offer real-time video streaming services. QoS makes for a seamless experience from the end of the user by prioritizing these applications over less time-dependent data packets.
6. Minimizing latency and jitter
One can use QoS technology and tools to smoothen the process and increase efficiency in areas where latency and jitter are a problem. It reduces delays in sending network requests and procession time and shortens the latency period. It also removes jitters from a service network.
7. Use in large-scale IoT projects and packet loss prevention
Finally, quality of service is becoming a highly researched topic in the IoT industry. With so many devices connected over a network, there has to be a traffic warden, directing the flow of data by priority and managing data traffic to ensure that all information reaches the cloud or necessary destination. The lack of QoS in IoT could result in information overload and chaos, to lose vital information.
See More: Distributed Computing vs. Grid Computing: 10 Key Comparisons
Takeaway
As networking and connectivity become increasingly more widespread, quality of service or QoS is an essential factor to remember. As a performance measure, it must be part of enterprise SLAs and govern how network and cloud vendors implement their solutions. Further, QoS tools are essential in connected landscapes like smart homes, smart campuses, and smart cities, ensuring that application traffic is correctly routed and prioritized.
Did this article help you understand the meaning and functionality of QoS? Tell us on LinkedIn, Twitter, or Facebook. We’d love to hear from you!
MORE ON IoT
- What Is the Internet of Things? Definition, Role, Examples, and Trends for 2022
- What Is IoT Device Management? Definition, Key Features, and Software
- What Is Network Management? Definition, Key Components, and Best Practices
- What Is Edge Computing? Components, Examples, and Best Practices
- Top 10 Edge Computing Platforms in 2022








